The Environmental in Morocco
The Urban population in 2022 is 64.6% of the total population with an estimated 1.88% annual rate of urbanization change between 2020-2025.
- As of 2017, Annual freshwater withdrawals were 10.431 billion cubic meters with .212 billion for industrial use, 1.063 billion for municipal use, and 9.156 billion for agricultural.
- 4.4% of the energy produced by Morocco is through hydroelectricity.
- Morocco also seeks to expand its renewable energy capacity with a goal of making renewable more than 50% of installed electricity generation capacity by 2030.
- 39.9% of the population has access to electricity according to World Bank (2020) with 71% of the urban population and 23% of the rural population with access to electricity. 65% of the energy produced by Algeria is through fossil fuels.


Downsides of Morocco in Environment
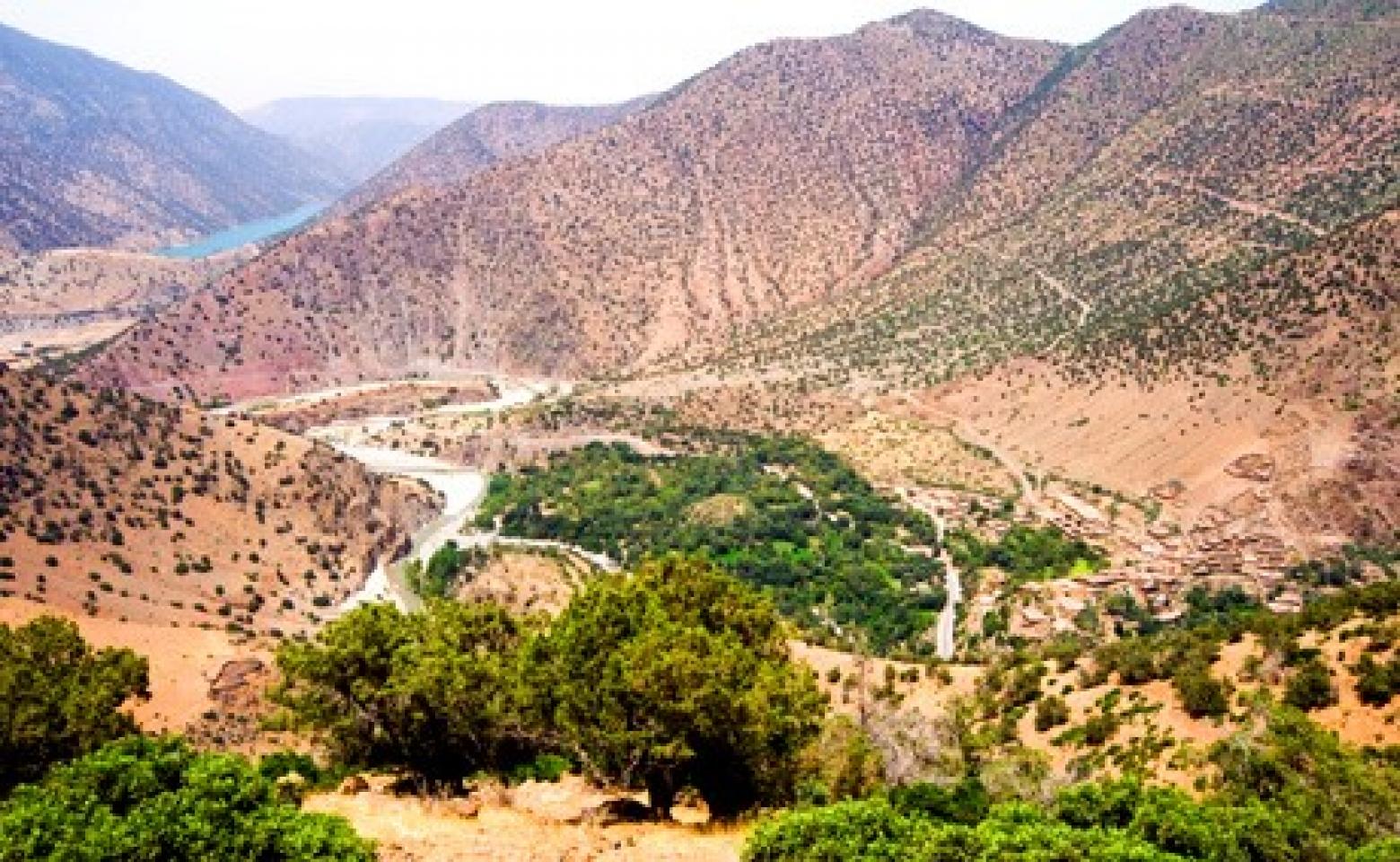
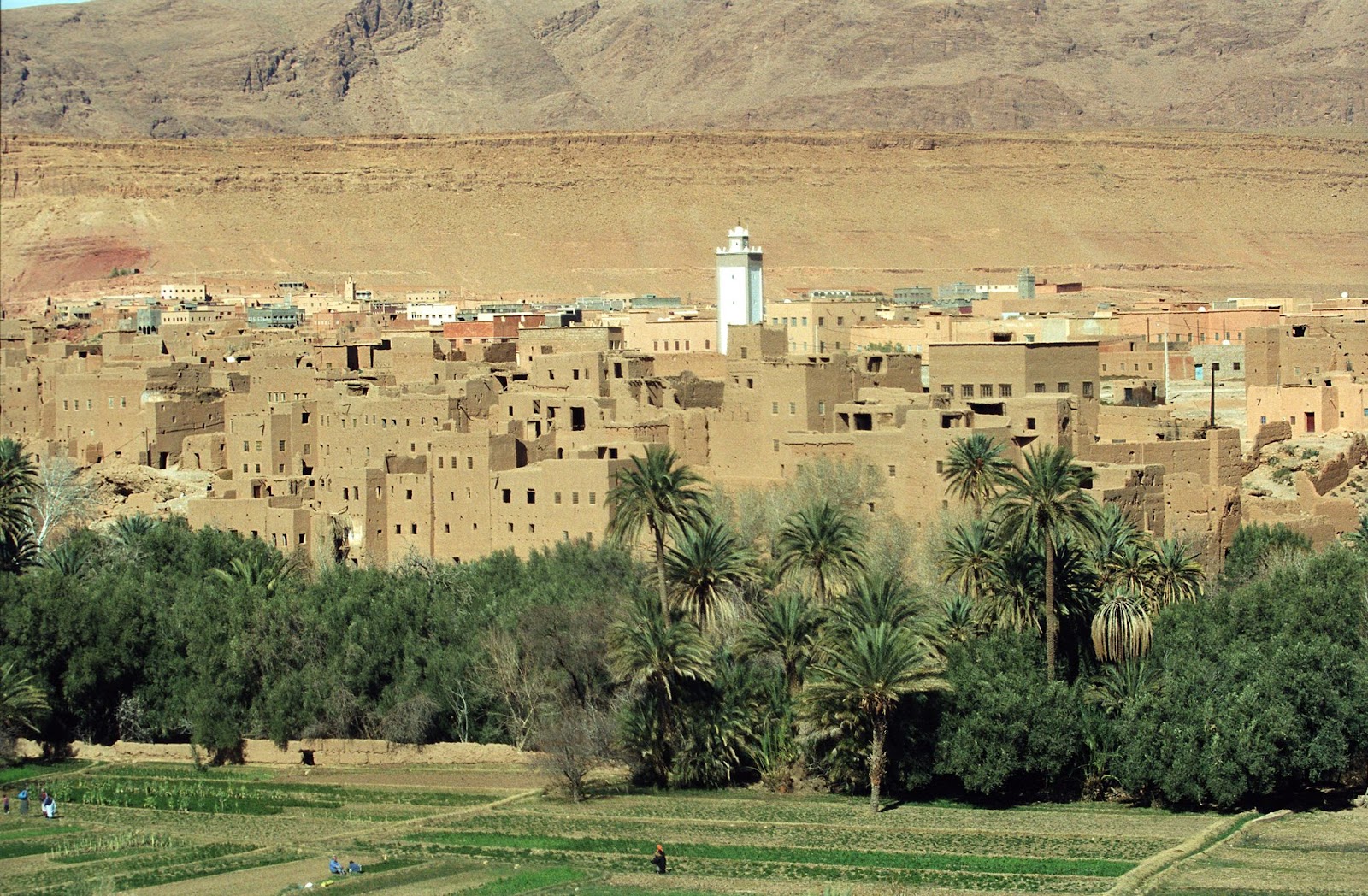
Morocco’s terrain is mountainous northern coast (Rif Mountains) and interior (Atlas Mountains) bordered by large plateaus with intermontane valleys, and fertile coastal plains; the south is mostly low, flat desert with large areas of rocky or sandy surfaces.
- As of August 2022, Morocco reported a total of 1,264,945covid cases with 55,300,000 of the population with at least one covid vaccine dose.
- Environmental issues are in the north, land degradation/desertification (soil erosion resulting from farming of marginal areas, overgrazing, destruction of vegetation).
- Water and soil pollution due to dumping of industrial wastes into the ocean and inland water sources, and onto the land; in the south, desertification; overgrazing; sparse water and lack of arable land.
- Co2 emissions for Morocco in 2019 wwere1.96 metric tons per capita in Co2 emissions and above the continent’s average of roughly 1 metric ton per capita(2020). In absolute terms, Morocco ranked 11th emitting 60.2 million metric tons of CO2 emissions in Africa in 2019.
- Municipal solid waste generated annually 6,852,000(2014) metric tons.
International Environmental agreements are Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Convention, Marine Dumping-London Protocol, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling.
- Morocco’s climate is Mediterranean in the north, becoming more extreme in the interior; in the south, hot, dry desert; rain is rare; cold offshore air currents produce fog and heavy dew.