The Socio-Culture Environment in Tanzania
Tanzania was Africa’s largest refugee-hosting country for decades, hosting hundreds of thousands of refugees from the Great Lakes region, primarily Burundi, over the last fifty years.
Regions and Languages
- Languages spoken in Tanzania are Kiswahili or Swahili (official), Kiunguja (the name for Swahili in Zanzibar), English (official, primary language of commerce, administration, and higher education), Arabic (widely spoken in Zanzibar), many local languages.
- Note – Kiswahili (Swahili) is the mother tongue of the Bantu people living in Zanzibar and nearby coastal Tanzania; although Kiswahili is Bantu in structure and origin, its vocabulary draws on a variety of sources including Arabic and English; it has become the lingua franca of central and eastern Africa; the first language of most people is one of the local languages
- There are many different religions in Tanzania. They are: Christian 63.1%, Muslim 34.1%, folk religion 1.1%, Buddhist <1%, Hindu <1%, Jewish <1%, other <1%, unspecified 1.6% (2020 est.)
- African 99% (of which 95% are Bantu consisting of more than 130 tribes), other 1% (consisting of Asian, European, and Arab); Zanzibar – Arab, African, mixed Arab and African.
- Human flight and brain drain index is 6.7/10 making it the 27th lowest in Africa and 50th highest globally in the year 2022.
- The age dependency ratio for Algeria is 86.79% ranking 14 in Africa and 14 globally (2021).
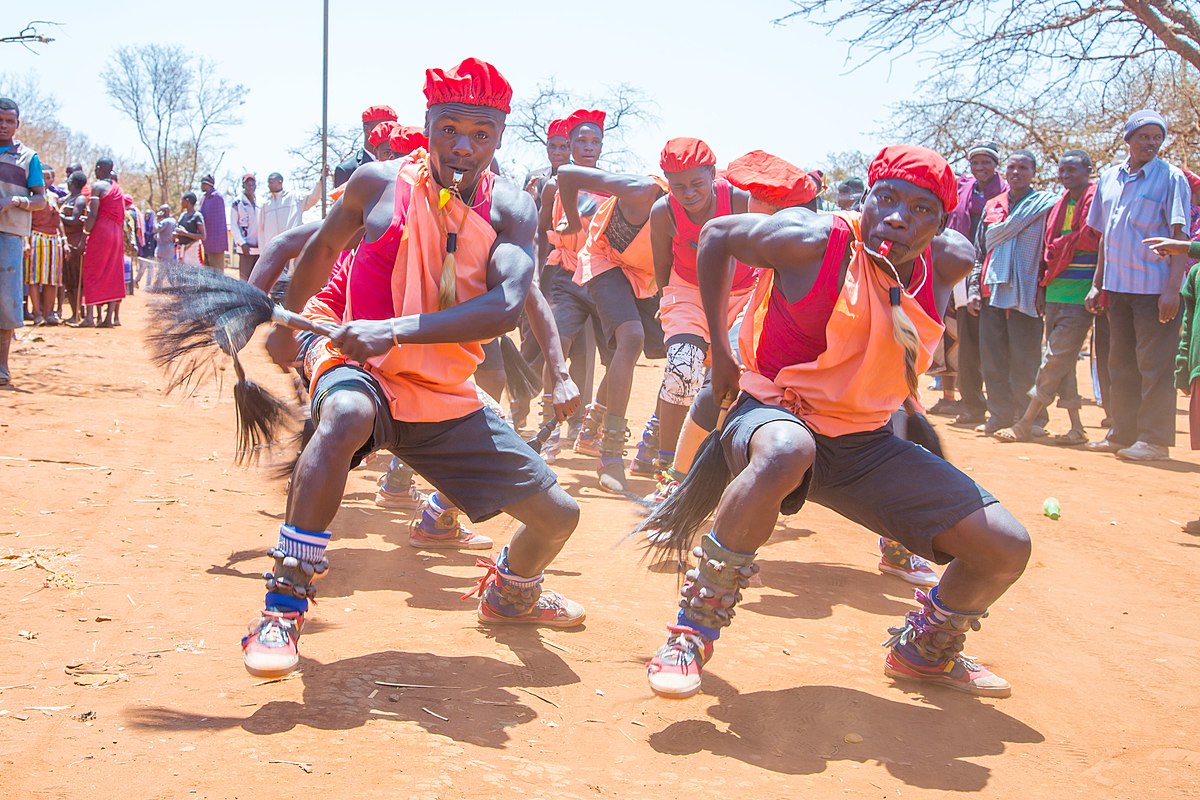

The Sukuma is the largest ethnic group in the country and represents around 16% of Tanzania’s total population. The vast majority of citizens, including many of the Sukuma, Hehe, and Nyakyusa peoples.
Population
- Population in Tanzania is about 63,852,892 (2022, 23rd most populous globally).
- Population Growth Annual Rate: 2.78% (2022)_ranked 13 globally
- Urban Population: 36.7% in the year 2022.
- Infant Mortality Rate: 30.87 per 1,000 births (2022)- ranked 49 globally.
- Life Expectancy at birth: 70.19 years (2020).
- 2.67% of the population aged 65 and above, is the 40th in Africa and 171st globally (2021).
- The maternal mortality per 100,000 live births is 524, making Tanzania the 6th in Africa and 14th globally (2017).
Negative impacts of the Socio-Culture in Tanzania
- Tanzania is increasingly a transit country for illegal migrants from the Horn of Africa and the Great Lakes region who are heading to southern Africa for security reasons and/or economic opportunities.
- Tanzania is a source, transit, and destination country for men, women, and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; the exploitation of young girls in domestic servitude continues to be Tanzania’s largest human trafficking problem.
- Significant transit country for illicit drugs in East Africa; international drug-trafficking organizations and courier networks transit through Tanzania to smuggle heroin and methamphetamine from Southwest Asia;
- Tanzania has 48 deaths of children under 5 years per 1000 live births, the 31st in Africa and the 36th globally (2020).
- Tanzania is ranked 160/191 on the Human Development Index(HDI) with a 0.549 value, a 0.001 increase from 2020, which is below the global average of 0.732 (2021). Tanzania’s HDI value is a Low Human Development Classification.
- Human flight and brain drain index is 6.7/10 making it the 27th lowest in Africa and 50th highest globally (2022).